What Is Scrum? | Key Elements of Scrum
Introduction
In the landscape of project management, "What Is Scrum" has become a frequent query among professionals seeking to adopt Agile methodologies. Scrum stands as a pivotal framework within Agile, reshaping the traditional approaches to project execution. Let's explore the essence of "What Is Scrum" and its foundational principles within Agile methodology.
Understanding What Is Scrum:
Scrum, fundamentally an Agile framework, fosters iterative and incremental development, focusing on adaptability and customer-centric approaches. Embracing Scrum involves adhering to its core principles, roles, events, and artifacts, enabling teams to navigate complex projects effectively.
Key Components of Scrum:
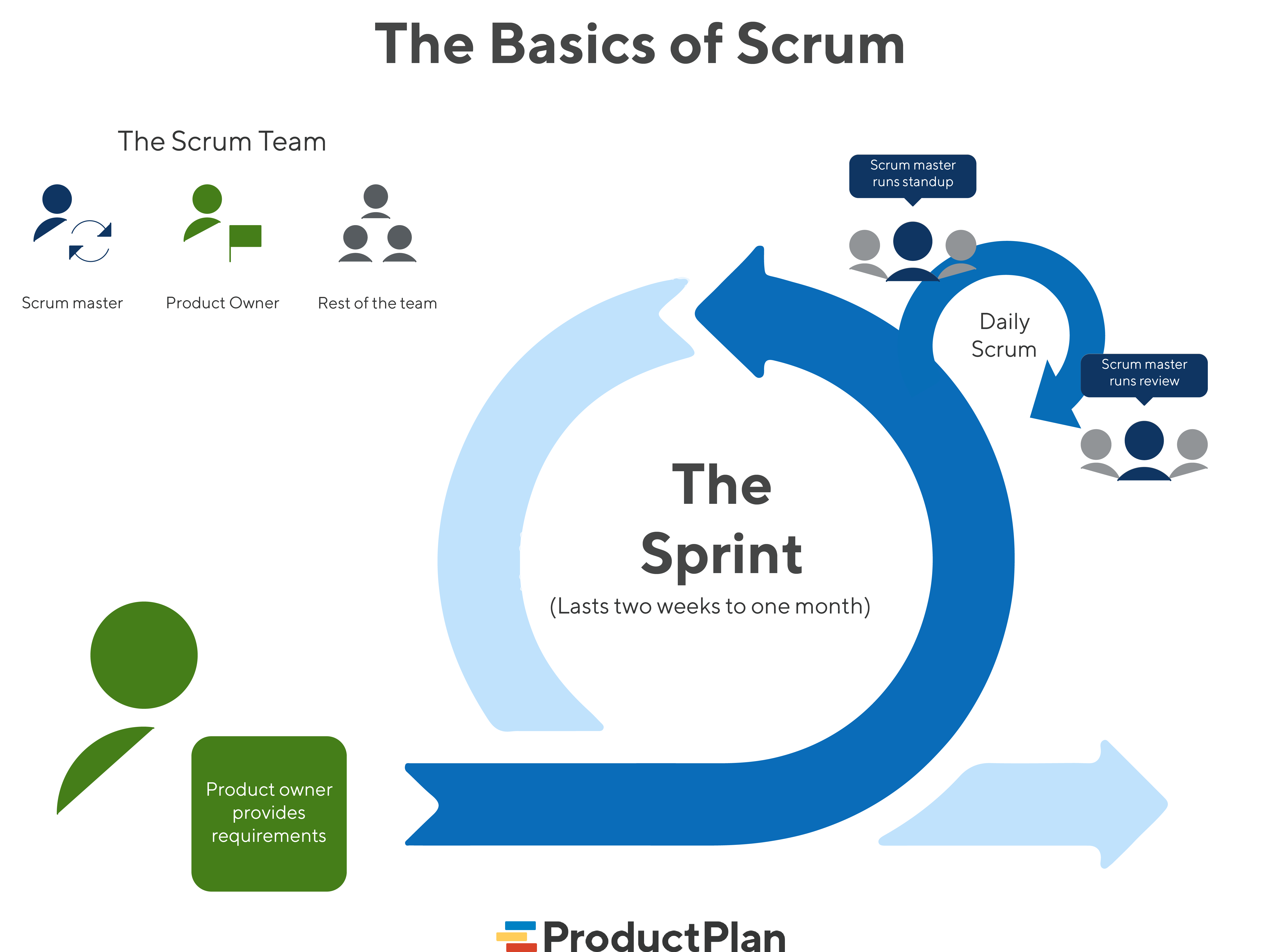
Scrum Roles:
Central to Scrum are three key roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team. The Product Owner champions stakeholder interests, setting priorities and ensuring deliverables align with their needs. The Scrum Master acts as a guide, facilitating the team and removing impediments. The Development Team comprises professionals responsible for product development.
Scrum Events:
Scrum events, or ceremonies, include Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-ups (Daily Scrum), Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective. These events facilitate planning, synchronization, review, and continuous improvement throughout the project lifecycle.
Scrum Artifacts:
Scrum artifacts encompass the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment. The Product Backlog captures all product requirements, the Sprint Backlog outlines items for a specific sprint, and the Increment represents the cumulative work completed during sprints.
Operational Dynamics of Scrum:
Scrum operates on the concept of time-boxed iterations called "Sprints," usually lasting 2-4 weeks. Sprints commence with Sprint Planning, where the team defines goals and plans work. Daily Stand-ups maintain alignment and address hurdles, ensuring transparency and collaboration.
Sprints culminate with the Sprint Review, showcasing completed work to stakeholders, followed by the Sprint Retrospective, enabling teams to reflect and enhance their processes continually.
Advantages of Embracing Scrum:
Adaptability: Scrum empowers teams to adapt swiftly to changing requirements, fostering flexibility in dynamic environments.
Enhanced Transparency: Regular meetings and visible progress foster transparency among stakeholders, nurturing trust and collaboration.
Continuous Improvement: Through retrospectives, teams refine processes, driving productivity and product quality improvements.
Conclusion:
In essence, understanding "What Is Scrum" involves grasping its essence as an Agile framework promoting adaptability, collaboration, and continuous improvement. Embracing Scrum revolutionizes project management methodologies, empowering teams to deliver value iteratively and effectively in today's fast-paced business landscape.
The profundity of Scrum transcends traditional project management, ushering in a culture of innovation, teamwork, and customer satisfaction, making it a cornerstone in modern organizational frameworks.
Comments
Post a Comment